
Hello {{first_name |there}},
In today’s edition:
• Selection biases in elite youth handball
• Daily mindfulness effects on sleep in judoka
• New way to assess Achilles tendon structure
• Development and relative age in handball
• Interval training boosts endurance in cyclists
• Carbohydrate impact on heat acclimation performance
• Gait analysis post ACL reconstruction
• Heart rate variability during military simulations
• Time of day effects on student behavior in PE
• Kinematic alignment vs. mechanical alignment in stance
and several more…
In focus: Understanding Selection Biases in Elite Youth Handball
In elite youth handball, selection biases stemming from relative age effects (RAEs) and maturation significantly influence player development and team composition, raising critical questions about inclusivity and talent identification equity. Recent 2025 research analyzing over 4,500 German youth handball players reveals that relatively younger players born later in the selection year must mature earlier than their peers to overcome inherent disadvantages, with effect sizes of g = 0.99 for females and g = 0.56 for males. However, this biological compensation only offsets approximately one-third of the relative age difference, leaving substantial systematic bias intact.
These findings complement earlier research showing striking odds ratios in talent selection - up to 8.2 for girls and 5.2 for boys favoring relatively older players at county and regional levels. The persistence of these biases extends beyond initial selection phases, as analysis of World Handball Championships data demonstrates continued overrepresentation of early-born athletes at elite international levels. Moreover, longitudinal studies tracking player development indicate that while some late-born players eventually succeed, the systematic exclusion during formative years limits the overall talent pool and may perpetuate performance inequalities.
For practitioners, addressing these biases requires comprehensive intervention strategies including coach education on relative age awareness, implementation of bio-banding approaches that group players by maturation rather than chronological age, and development of sport-specific assessment tools that minimize physical maturity advantages. Current research suggests that German handball federations are actively developing solutions to these challenges, recognizing that equitable talent identification systems are essential for optimizing both individual player development and the sport’s competitive integrity.

-Haresh 🤙
A message from our sponsor
Can’t think clearly?
Struggling to stay focused? Crashing before the day ends?
You can change what happens next.
Take our free 3 minute questionnaire
Track hidden causes of brain fog
Go further with our clinical team
You can finally get clear steps to bring back mental clarity.
With Superpower.

Want to learn how to create compelling data visualizations that expose selection bias patterns in youth sports?
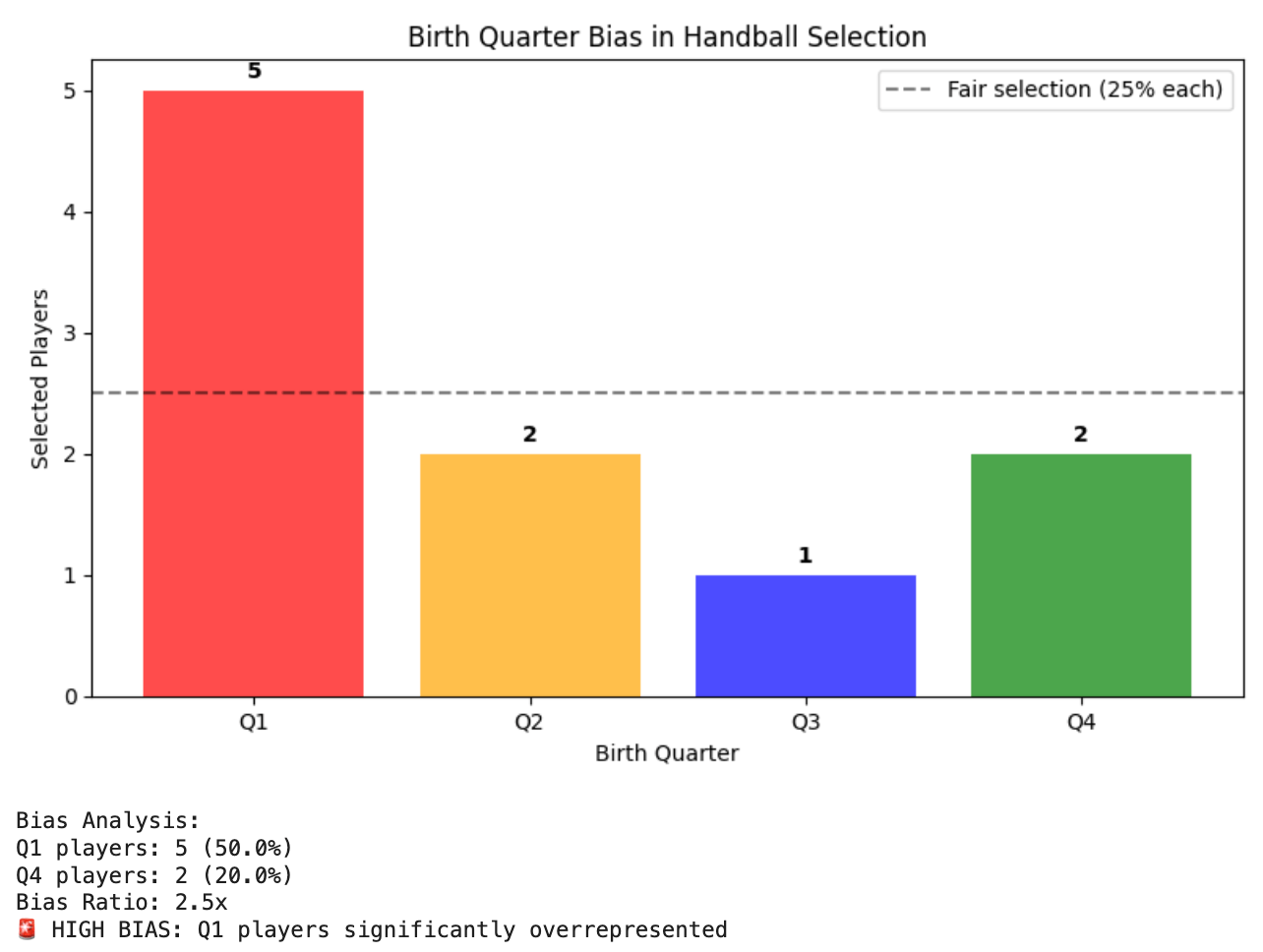
This hands-on exercise teaches you to analyze birth quarter distributions and calculate bias ratios using the Matplotlib library in Python. Access the full interactive lesson on Google Colab.

Key finding:
Early maturation helps relatively younger youth handball players overcome selection biases based on age and maturation.
How they did it:
Methodology: The study analyzed a dataset of 2,259 female U15 and 2,340 male U16 handball players from the German Handball Federation, utilizing factors such as birth date, body mass, body height, and sitting height to assess maturation and relative age effects.
Results: Male players exhibited a significant maturation bias, maturing approximately one year earlier than the average for German boys (g = -1.67), while females showed no such bias (g = 0.18). Furthermore, relative age biases were confirmed, showing a higher likelihood of selection for players born in earlier quarters of the year.
Key Findings: An analysis demonstrated that relatively younger players born later in the selection year mature earlier than their older peers, with effect sizes of g = 0.99 for females and g = 0.56 for males, indicating a compensatory adjustment to overcome relative age disadvantages.
Innovations: The research highlighted the importance of objective biological age assessments in player selection and emphasized the need for awareness among coaches regarding relative age effects to ensure more equitable talent identification.
Implications: The findings underscore the need for improved selection processes that consider both maturation and relative age, allowing for a more comprehensive approach to talent development in youth handball and potentially reducing biases in coaching and competition.
Why it matters:
These findings highlight the importance of considering maturation and relative age effects in talent selection for youth handball. Notably, male players mature nearly a year earlier than their peers, and relatively younger players born later in the selection year tend to mature earlier to combat selection disadvantages.
A message from our sponsor
Seniors Everywhere Are Switching to This $99 Hearing Aid
Oricle Hearing gives you crystal-clear sound, wireless charging, and all-day battery life for under $100. No doctor visits, no crazy prices—just amazing hearing at an unbeatable deal.
Discover how these affordable hearing aids are changing the lives of people everyday.
Key finding:
Mindfulness significantly improves sleep quality and recovery-stress states in elite judoka athletes.
How they did it:
Methodology: The study involved 33 elite judoka (17 females, 16 males, average age 23.79) monitored over two weeks using both objective actigraphy and subjective self-report protocols to assess sleep quality, training loads, and mindfulness levels daily.
Results: Multilevel analyses indicated that higher daily mindfulness (measured via the acting with awareness facet) was linked to longer subjective total sleep time (S-TST) and shorter subjective sleep onset latency (S-SOL), with trait mindfulness associated with shorter objective sleep onset latency (O-SOL).
Recovery-Stress Findings: Daily mindfulness positively influenced recovery-stress states in the evening, where higher mindfulness scores correlated with higher perceived recovery and lower stress levels in the following morning assessments.
Innovations: By integrating both objective (actigraphy) and subjective (sleep diaries) assessments, the study revealed distinct influences on qualitative (e.g., perceived restfulness) and quantitative (e.g., sleep duration) sleep parameters, highlighting the need for multifaceted approaches in sleep research.
Additional Insight: The study suggests a negative impact from higher numbers of training sessions and session intensity on sleep quality, indicating the potential benefits of integrating mindfulness practices into athletes’ routines for better recovery and sleep outcomes.
Why it matters:
Understanding the relationship between mindfulness and sleep can greatly benefit elite athletes and their coaches. This study found that athletes with higher levels of mindfulness experienced improved sleep quality and recovery, with a notable association between mindfulness and shorter sleep onset latencies. With 90% of athletes reporting subjective sleep problems, incorporating mindfulness practices could offer simple yet effective interventions to enhance performance and well-being in high-pressure training environments.

Biomechanics
-A novel ultrasound method reliably identifies the locations of individual subtendons in the Achilles tendon, aiding injury treatment.
Biomechanics
-Gait biomechanics significantly differ between reconstructed and nonsurgical limbs in patients post quadriceps tendon ACL reconstruction.
Biomechanics
-Kinematic alignment in knee surgeries yields a tibial joint line angle closer to parallel than mechanical alignment.
Nutrition
-A high-carbohydrate diet improves running performance in the heat after short-term heat acclimation.
Physical Education and Pedagogy
-Afternoon physical education classes significantly reduce disruptive behaviors in middle school students compared to morning sessions.
Sport Physiology
-Moderate-intensity interval training significantly enhances endurance performance in well-trained cyclists compared to regular training.
Sport Physiology
-Exercise during military operations increases heart rate variability, indicating parasympathetic activation, regardless of testosterone supplementation.
Talent Identification and Development
-Long-term development in handball varies by gender and is influenced by players’ relative age effects.



